Linux - Install
-
Java 8+ (server), Java 6+ (client)
-
Dual-Core Processor (32 or 64 bit)
-
4GB RAM
-
10GB free HD space
Also, it is assumed that you are familiar with operating a shell, and you have root or superuser privileges to run the Ignition installer.
To Download and Install Ignition on Linux
-
Go to the Inductive Automation website at
www.inductiveautomation.com -
Select Download > Current Release.
-
On the Ignition Downloads page, scroll down to System Installers and select the
ignition-X.X.X-linux-x64-installer.run installer.
If your computer runs on a 32- bit Linux, select the ignition-X.X.Xlinux-32-installer.run.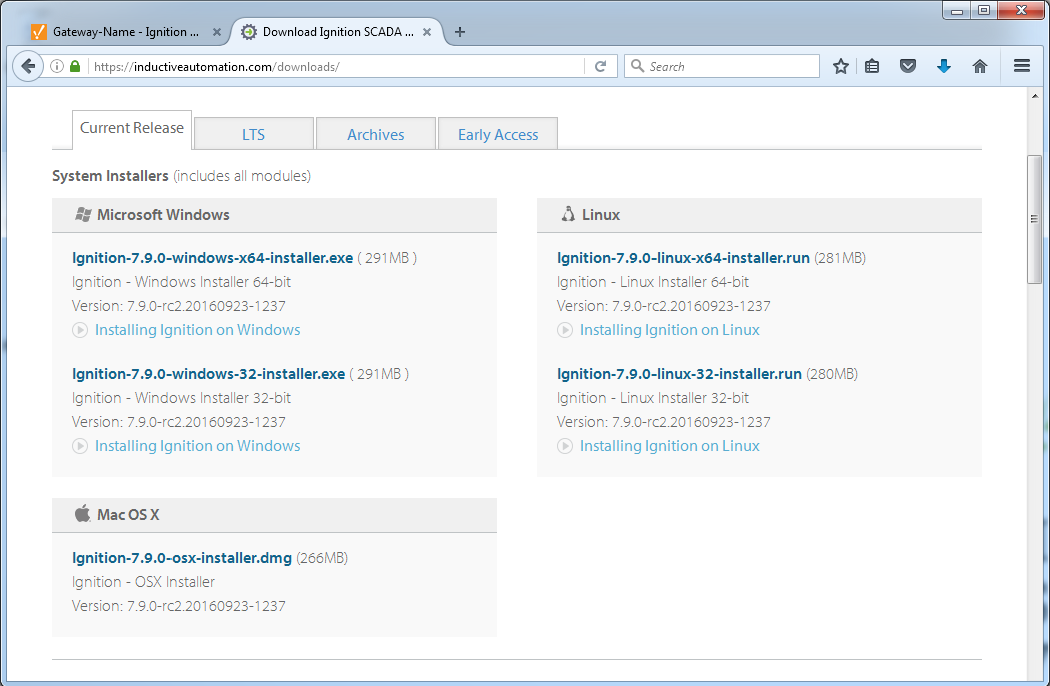
Note: If you choose the wrong installer, an Error window is displayed letting you know the correct installer to use for your machine.
The installers can run in both graphical or command-line mode, allowing Ignition to install on a headless Linux server. The installer will install files in the following locations:
/usr/local/bin/ignition
(unless a different installation directory was used) – contains binaries, startup scripts and the uninstall executable
/var/lib/ignition/data
contains application-generated files, temporary files and the internal database
/var/lib/ignition/user-lib
contains modules and JDBC jars
/var/log/ignition
contains the wrapper.log and other log files
/etc/ignition
contains configuration files. Symbolic links to these files are created in
/var/lib/ignition/data -
You must run all the commands as root. Prefix everything with sudo or first run
sudosu -
If Java 8 is not already installed, run the following commands to install it:
sudoadd-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/javasudoapt-get updatesudoapt-getinstalloracle-java8-installer -
Open a command shell and navigate to the installer executable, by running the following command from the command line:
sudochmod+x ignition-x.x.x-linux-xxxinstaller.run -
Start the installer executable.
The installer can run in a graphical mode or command line mode.
If you are running the installer in a shell in a graphical environment, the graphical installer opens automatically.
If you are running the installer in a headless Linux installation or through an SSH shell, the text installer opens automatically.
To start the text installer in a graphical environment, run the following command:sudo./ignition-X.X.X-linux-xxx-installer.run --mode text -
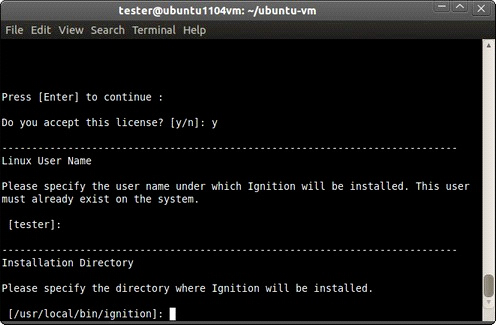
Agree to the licensing terms.
-
Ensure the installation directory is the default directory at:
/user/local/bin/ignition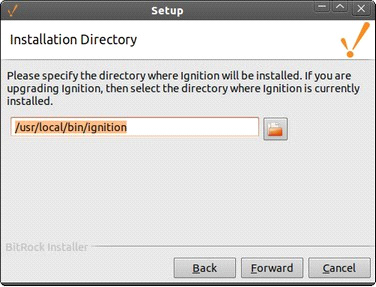
-
Specify the user name under which Ignition is to be installed. For Ubuntu installations, the user that invoked sudo is used by default. For other Linux installations, this field is initially blank.
The Linux installer requires a user name to set the permissions on the folders created by the installer. This user is then able to start and stop Ignition, run the Gateway Control Utility, and the command line interfaces.
The binaries in the installation folder are still owned by root and cannot be modified without root access. The selected user must already exist on the system before starting the installer.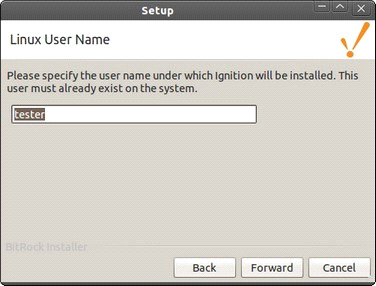
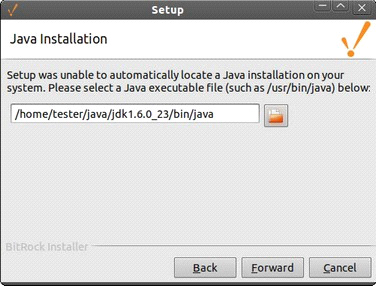
Normally, the installer is capable of auto-detecting a Java 8 installation that has been installed through APT or some other Linux package management tool. In these cases, the installer uses that Java installation and skips this step.
However, if you have installed Java by extracting the Java binaries to a folder and adding them to the system PATH, the installer is unable to find the Java binaries. You must provide the installer with a full path to the Java executable. -
If the Java Installation window is displayed, type the full path to the Java executable.
-
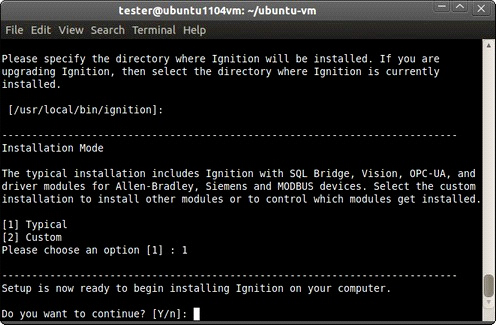
Select either the Typical or the Custom installation mode.
The Typical mode installs everything that you need to get started.
The Custom mode lets you add optional modules, such as the OEE Downtime module. It also lets you control and select which modules get installed.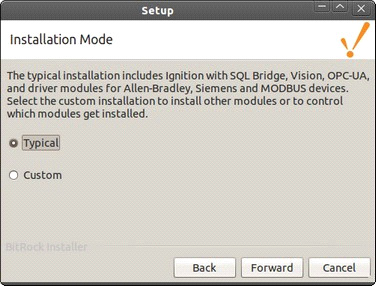
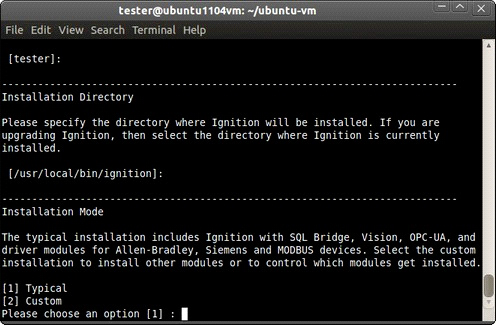
If you select Custom Mode, the Select Components window is displayed.
• In Graphical mode to view a brief description of the module, click on the module name. Selecting the check box next to a module installs the module as part of the Ignition installation. Clearing the check box next to a module prevents the module from being installed.
• In Text mode a list of all the modules are displayed one at a time. Type y to install the module, and type n to prevent the module from being installed.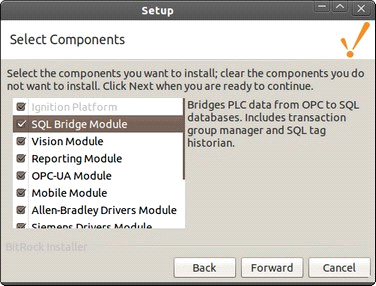
Ignition is now ready to be installed. At this point, you can click the Back button (graphical mode) to change your selections. For the text mode, you can only abort the installation at this point by typing n.
-
Click Forward (graphical mode) or type y (text mode) to finish the installation.
-
When the installation is complete, click Finish (graphical mode) or type y to start Ignition (text mode).
Ignition is started as a background process.
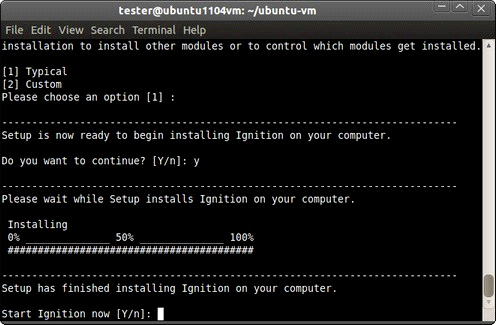
Once the Ignition Gateway starts up, your web browser opens and brings you to the Gateway home page at http://localhost:8088.
Ignition Service
Stop and Start Ignition
After installation, you can start and stop Ignition with the following commands:
/etc/init.d/ignition start/etc/init.d/ignition stopRemove Service
When installing under Ubuntu, Ignition starts automatically whenever the computer reboots. If you wish to stop this behavior, you need to use the update-rc.d tool to remove the service (uninstalling Ignition also removes the service) as follows:
/etc/init.d/ignition stopupdate-rc.d -f ignition removerm /etc/init.d/ignitionWhen installing under other Linux distributions, use that distribution's method to automatically start a program after reboot.
For example, this command auto-starts Ignition installed in a Fedora 15 system (run as root user):
chkconfig --level 2345 ignition onSet the system PATH
For Ubuntu installations, the installation directory is automatically appended to the system PATH. You can start programs like the Gateway Control Utility from the command line without specifying a complete path to the installation directory.
Note that after installation, you need to close and reopen the command shell for the PATH change to take effect. For other Linux installations, you need to manually add /usr/local/bin/ignition (or your installation directory) to any script that can set the system PATH (such as .profile or .bashrc).
Automated Installation on Linux
You can automate Ignition installation across different machines using scripts. Ignition is then installed silently from a command shell without showing any user prompts.
Keep in mind that the installer cannot automatically start the Gateway after a silent installation. Use the /etc/init.d/ignition start command as shown in example below.
Command line example
sudo ./ignition-7.x.x-linux-x64-installer.run --mode unattended --prefix /somefolder/bin/ignition --unattendedmodeui none/etc/init.d/ignition startFlags
-- mode unattended (ensures that no prompts appear during installation)
-- prefix /somefolder/bin/ignition (optional flag; if a value is set, then Ignition is installed in the specified folder, otherwise Ignition is installed in /usr/local/bin/ignition by default)
-- serviceuser username (allows a Linux system user to be installed (that is, a user that cannot log in to the OS))
-- unattendedmodeui none | minimal (the none flag does not display any sort of graphic during installation; the minimal
flag displays a small progress bar and nothing else)
Uninstalling Ignition on Linux
Be sure to back up your Gateway and unactivate your Gateway license.
During a new Ignition installation, an uninstaller executable is created.
When Ignition is uninstalled, the settings database and folder in /data is backed up to /data_<current date>, and modules and user-supplied JDBC jars in /user-lib are backed up to /user-lib_<current date>. Also, the Ignition service is removed from Ubuntu Linux installations automatically.
Linux – Using Downloaded Installer
Ignition 7.3 or later installations on Linux contain an uninstaller executable.
To run the uninstaller,
-
Open a command shell and navigate to /user/local/bin/ignition (or your installation folder).
-
As root or sudo, run
./uninstall
Linux Ignition installations before 7.3 used a zip file that did not form an installation. Since these installations were never created with an installer executable, no uninstaller executable was ever generated. This is true even if using a 7.3 or later installer executable to upgrade an installation from before 7.3. For installations before 7.3, you must manually remove the Ignition folders using the commands below.
/etc/init.d/ignition stop*Ubuntu only* update-rc.d -f ignition remove rm /etc/init.d/ignition rm -rf /usr/local/bin/ignition *Recommended* mv /var/lib/ignition/data /var/lib/ignition/data_<current date> *Recommended* mv /var/lib/ignition/user-lib /var/lib/ignition/user_lib_<current date> *Recommended* mv /etc/ignition /etc/ignition_<current date> rm -rf /var/log/ignition
Similar Topics ...